1. HSP – Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia
- This is a group of genetic disorders that mainly cause weakness and stiffness in the legs.
- “Hereditary” means it’s usually passed down in families.
- “Spastic” means muscles are tight or stiff.
- “Paraplegia” means that the legs are affected.
2. SPG4 – A Specific Type of HSP
- There are many types of HSP. SPG4 is the most common type.
- It’s caused by problems in a gene called SPAST (also known as spastin).
- The SPAST gene helps make a protein that helps cells work properly, especially nerve cells.
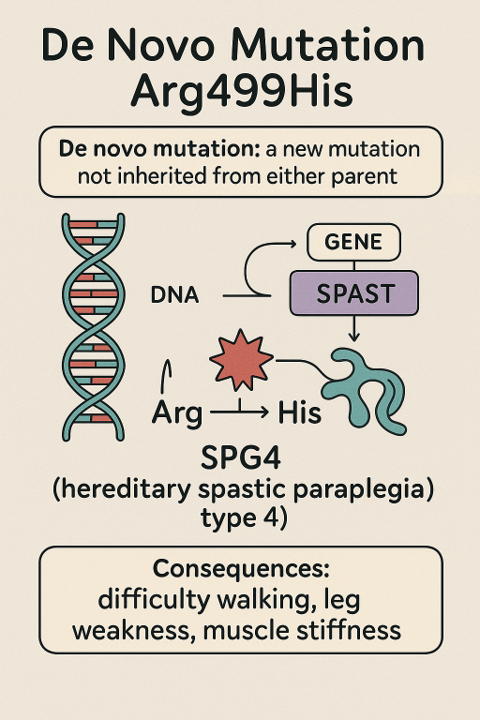
3. De novo – New Mutation
- “De novo” means this mutation happened for the first time in the person.
- It was NOT inherited from either parent.
4. Arg499His – The Specific Change in the Gene
- Genes are like instructions made of letters.
- “Arg” stands for arginine, and “His” stands for histidine – both are building blocks of proteins.
- At position 499 in the protein, the instruction for arginine (Arg) has been changed to histidine (His).
- This single change can cause the protein to not work properly.
🔬 What Happens Because of This Mutation?
- The mutated SPAST gene leads to a faulty spastin protein.
- This protein normally helps “clean up” and maintain nerve cells, especially ones going to the legs.
- When it doesn’t work right, nerve cells break down or stop working well.
- This causes muscle stiffness, weakness, and walking problems over time.
Summary:
HSP SPG4 De novo Arg499His is a genetic condition where a child (with no family history) has a new change in their SPAST gene. This change at spot 499 in the gene causes the legs to become weak and stiff due to nerve problems.
The diagram below shows how a single letter change in the DNA leads to the Arg499His mutation and results in problems in nerve function.
Leave a reply